Smart contract-controlled payment module that facilitates peer-to-peer purchase of equipment as well as payment for MineBee partners premium services. A marketplace for pricing, buying and selling second-hand mining equipment and for providing price comparisons of new equipment. MineBee is developing a turnkey solution that will address the mining industries multi-faceted problems and supply participants with real-time network analysis which drives and maximizes efficiencies and profitability across the board.
Moreover, we derive the revolution of mining market network for miners to have full scalability of their mining ecosystem. Blockchain is an inevitable technology for MineBee to enable transparency and security between not only companies and users, but P2P trading.
Mining Bitcoin
It is our primary currency within the MineBee ecosystem. This event is called the halving or the "halvening. This process is designed so that rewards for Bitcoin mining will continue until about Once all Bitcoin is mined from the code and all halvings are finished, the miners will remain incentivized by fees that they will charge network users. The hope is that healthy competition will keep fees low. This system drives up Bitcoin's stock-to-flow ratio and lowers its inflation until it is eventually zero.
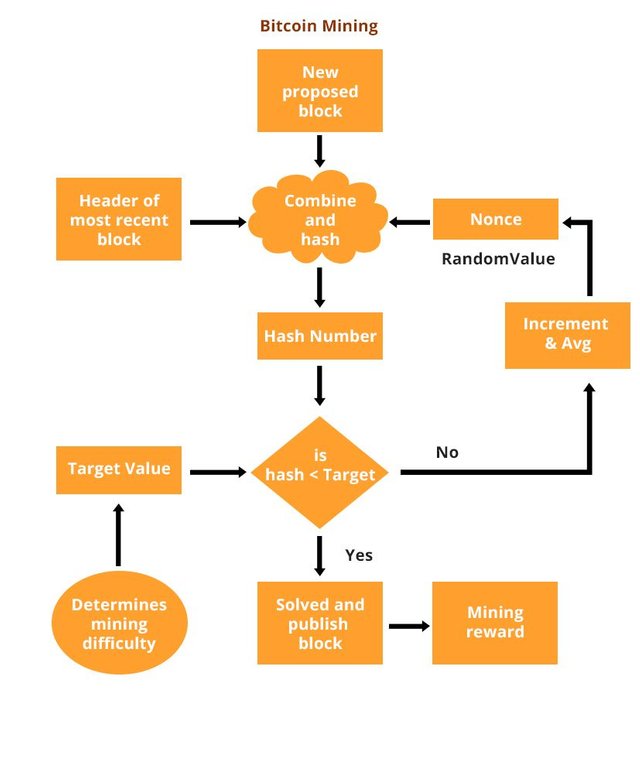
After the third halving that took place on May 11th, , the reward for each block mined is now 6. Here is a slightly more technical description of how mining works. The network of miners, who are scattered across the globe and not bound to each other by personal or professional ties, receives the latest batch of transaction data. They run the data through a cryptographic algorithm that generates a "hash," a string of numbers and letters that verifies the information's validity but does not reveal the information itself.
In reality, this ideal vision of decentralized mining is no longer accurate, with industrial-scale mining farms and powerful mining pools forming an oligopoly. More on that below. Given the hash c2c4dfbd55d64f1a7c22ffeb66e15eca30, you cannot know what transactions the relevant block contains. You can, however, take a bunch of data purporting to be block and make sure that it has not been tampered with.
If one number were out of place, no matter how insignificant, the data would generate a totally different hash. As an example, if you were to run the Declaration of Independence through a hash calculator , you might get fcaa4bc84e2bafec76ace5da68cf5c36bd3f Delete the period after the words "submitted to a candid world," though, and you get e4fdca4c5efcdcd4cffcab93f60f82f23f97c4. This is a completely different hash, although you've only changed one character in the original text.
The hash technology allows the Bitcoin network to instantly check the validity of a block. It would be incredibly time-consuming to comb through the entire ledger to make sure that the person mining the most recent batch of transactions hasn't tried anything funny. Instead, the previous block's hash appears within the new block.
- bitcoin presentation powerpoint.
- bitcoin annual rate of return!
- Hoe werkt het Bitcoin-netwerk? | Mao Lal | Bitcoin, Neon signs, Hoe.
- The basics for a new user!
- The Most Liked Findings.
- bitcoin mining energy efficiency.
If the most minute detail had been altered in the previous block, that hash would change. Even if the alteration was 20, blocks back in the chain, that block's hash would set off a cascade of new hashes and tip off the network. Generating a hash is not really work, though. The process is so quick and easy that bad actors could still spam the network and perhaps, given enough computing power, pass off fraudulent transactions a few blocks back in the chain. So the Bitcoin protocol requires proof of work. It does so by throwing miners a curveball: Their hash must be below a certain target.
That's why block 's hash starts with a long string of zeroes. It's tiny. Since every string of data will generate one and only one hash, the quest for a sufficiently small one involves adding nonces "numbers used once" to the end of the data. So a miner will run [thedata]. If the hash is too big, she will try again. Still too big. Finally, [thedata] yields her a hash beginning with the requisite number of zeroes. The mined block will be broadcast to the network to receive confirmations, which take another hour or so, though occasionally much longer, to process.
Again, this description is simplified. Blocks are not hashed in their entirety, but broken up into more efficient structures called Merkle trees. Depending on the kind of traffic the network is receiving, Bitcoin's protocol will require a longer or shorter string of zeroes, adjusting the difficulty to hit a rate of one new block every 10 minutes. As of October , the current difficulty is around 6. As this suggests, it has become significantly more difficult to mine Bitcoin since the cryptocurrency launched a decade ago. Mining is intensive, requiring big, expensive rigs and a lot of electricity to power them.
And it's competitive. There's no telling what nonce will work, so the goal is to plow through them as quickly as possible. Early on, miners recognized that they could improve their chances of success by combining into mining pools, sharing computing power and divvying the rewards up among themselves. Even when multiple miners split these rewards, there is still ample incentive to pursue them.
Une question ?
Every time a new block is mined, the successful miner receives a bunch of newly created bitcoin. At first, it was 50, but then it halved to 25, and now it is The reward will continue to halve every , blocks, or about every four years, until it hits zero.
- How Bitcoin Works.
- Image result for monero currency symbol | Cryptocurrency, Bitcoin logo, Blockchain.
- is gpu bitcoin mining worth it.
- GET UP TO $132!
- bitcoin wallpaper phone!
- is bitcoin dying out.
At that point, all 21 million bitcoins will have been mined, and miners will depend solely on fees to maintain the network. When Bitcoin was launched, it was planned that the total supply of the cryptocurrency would be 21 million tokens. The fact that miners have organized themselves into pools worries some. They could also block others' transactions. Simply put, this pool of miners would have the power to overwhelm the distributed nature of the system, verifying fraudulent transactions by virtue of the majority power it would hold.
To go back and alter the blockchain, a pool would need to control such a large majority of the network that it would probably be pointless. When you control the whole currency, who is there to trade with? When Ghash. Other actors, such as governments, might find the idea of such an attack interesting, though. But, again, the sheer size of Bitcoin's network would make this overwhelmingly expensive, even for a world power.
Hoe kan ik Bitcoins kopen (BTC)? Alles over bitcoin kopen! ()
Another source of concern related to miners is the practical tendency to concentrate in parts of the world where electricity is cheap, such as China, or, following a Chinese crackdown in early , Quebec. For most individuals participating in the Bitcoin network, the ins and outs of the blockchain, hash rates and mining are not particularly relevant. Outside of the mining community, Bitcoin owners usually purchase their cryptocurrency supply through a Bitcoin exchange.
These are online platforms that facilitate transactions of Bitcoin and, often, other digital currencies. Bitcoin exchanges such as Coinbase bring together market participants from around the world to buy and sell cryptocurrencies.
These exchanges have been both increasingly popular as Bitcoin's popularity itself has grown in recent years and fraught with regulatory, legal and security challenges. With governments around the world viewing cryptocurrencies in various ways — as currency, as an asset class, or any number of other classifications — the regulations governing the buying and selling of bitcoins are complex and constantly shifting. Perhaps even more important for Bitcoin exchange participants than the threat of changing regulatory oversight, however, is that of theft and other criminal activity.
While the Bitcoin network itself has largely been secure throughout its history, individual exchanges are not necessarily the same. Many thefts have targeted high-profile cryptocurrency exchanges, oftentimes resulting in the loss of millions of dollars worth of tokens. The most famous exchange theft is likely Mt. Gox, which dominated the Bitcoin transaction space up through Well, actually your computer or node has to do some work! This work involves the confirming and checking of transactions which I talked about in the last section. Purchasing Dogecoin takes much less effort, especially when using Binance or Kraken.
This is the time when Dogecoin reached its all-time high and keeps increasing in price significantly. So if you do it now, you might still get on that train! Lots of computers work on the same block of transactions at the same time but the only one can win the reward of new coins.
All-in-one solution for advanced smart cryptocurrency mining
The one that earns the new coins is the node that adds the new block of transactions to the old block of transactions. This is completed using complex mathematical equations. The node that solves the mathematical problem first wins!
It can then attach the newly confirmed block of transactions to the rest of the blockchain. Most cryptocurrency mining happens this way. However, Dogecoin mining differs from other coins in several important areas.
These areas are :. Now, let's compare how DogeCoin mining works compared to Litecoin and Bitcoin Source : www. Bitcoin uses SHA to guide the mining of new currency and the other two use Scrypt. This is an important difference because Scrypt mining needs a lot less power and is a lot quicker than SHA This makes mining easier for miners with less powerful computers. Fans of Litecoin and Dogecoin think that they are fairer than Bitcoin because more people can mine them.